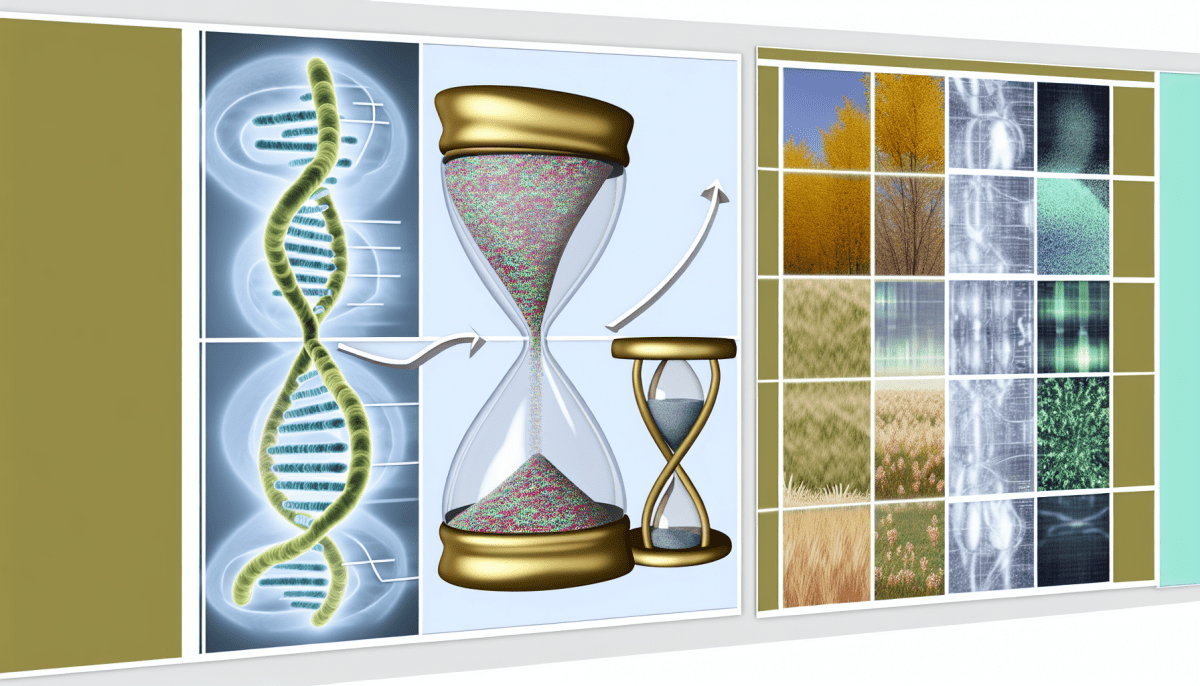
Telomeres are like the protective caps on the ends of your shoelaces, but instead of keeping your laces from fraying, they keep your chromosomes from unraveling. These tiny structures are made up of repeating patterns of DNA that act as a buffer to protect the genetic material in your cells. Just like how your shoe laces wear down over time, telomeres also shorten each time your cells divide.
As you age, your cells divide and replicate to replenish the tissues in your body. With each division, a small portion of the telomeres gets snipped off, eventually reaching a critically short length. When this happens, the cell enters a state known as replicative senescence, where it can no longer divide and function properly. This process is thought to be a crucial contributor to the aging process.
Some researchers believe that maintaining the length of telomeres could potentially slow down aging and extend lifespan. While there is still much to be learned about telomeres and their impact on aging, it is clear that they play a significant role in the overall health and longevity of our cells. By understanding how telomeres work, scientists are hopeful that we may one day unlock the secrets to slowing down the aging process.
How Telomeres Impact Aging
Telomeres are sections of DNA at the end of our chromosomes that act as protective caps to prevent the loss of important genetic information during cell division. Over time, these telomeres naturally shorten with each cell division, eventually reaching a critically short length where cells can no longer divide and may die. This process is a key factor in the aging of our cells and tissues.
As telomeres shorten, cells become more susceptible to damage and mutations, leading to a decline in their function and integrity. This can result in a variety of age-related health issues, such as increased risk of chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders. Additionally, shortened telomeres have been linked to a weakened immune system and slower wound healing, further contributing to the aging process.
Research has shown that lifestyle factors such as stress, lack of exercise, poor diet, and smoking can accelerate the shortening of telomeres, leading to premature aging. On the other hand, healthy habits like regular exercise, a nutritious diet, stress management, and sufficient sleep have been shown to slow down the rate of telomere shortening and possibly even reverse it. Understanding the impact of telomeres on aging can help us make informed decisions about our health and well-being to promote longevity and healthy aging.
Ways to Preserve Telomere Length
Preserving the length of telomeres, the protective caps at the end of our chromosomes, is crucial for maintaining overall health and potentially slowing down the aging process. Here are some simple ways to help keep your telomeres healthy and robust.
1. Eat a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients. Foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are high in antioxidants, which help protect telomeres from oxidative stress. Additionally, consuming omega-3 fatty acids from fish or flaxseed can also support telomere health.
2. Exercise regularly to boost telomerase activity. Telomerase is an enzyme that helps maintain telomere length, and studies have shown that physical activity can increase levels of telomerase in the body. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking or jogging, most days of the week.
3. Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. Chronic stress can accelerate telomere shortening, so finding healthy ways to cope with stress is essential for preserving telomere length and overall well-being.
The Connection Between Telomeres and Longevity
Telomeres are tiny protective caps at the end of our chromosomes that play a crucial role in the aging process. Think of them as the plastic tips on shoelaces that prevent them from fraying. As we age, our telomeres naturally shorten every time our cells divide. When they become too short, our cells can no longer divide, leading to cellular aging and eventually cell death.
Research has shown that the length of our telomeres is directly linked to our lifespan. Shorter telomeres have been associated with a higher risk of age-related diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and dementia. On the other hand, longer telomeres are often found in individuals with better health and increased longevity. This has led scientists to speculate that maintaining the length of our telomeres could potentially slow down the aging process and increase our lifespan.
There are several lifestyle factors that have been shown to influence telomere length. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and managing stress levels have all been linked to longer telomeres. Additionally, certain supplements and medications have been studied for their potential to prevent telomere shortening. While more research is needed to fully understand the connection between telomeres and longevity, the evidence so far suggests that taking care of our telomeres could be key to a longer and healthier life.